单选题 (共 6 题 ),每题只有一个选项正确
设函数 $f(x)=2 \ln x-\frac{1}{2} x^2+x$ 的图象在 $x=1$ 处的切线为 $l$, 则 $l$ 在 $x$ 轴上的截距为
$\text{A.}$ $-\frac{3}{4}$
$\text{B.}$ $\frac{3}{4}$
$\text{C.}$ $\frac{3}{2}$
$\text{D.}$ $-\frac{3}{2}$.
函数 $f(x)=\frac{3^x \cos 6 x}{3^{2 x}-1}$ 的图象大致为
$\text{A.}$ 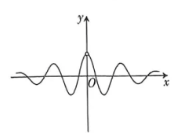 $\text{B.}$
$\text{B.}$ 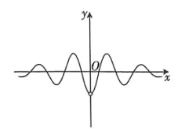 $\text{C.}$
$\text{C.}$ 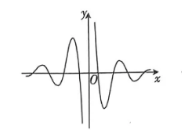 $\text{D.}$
$\text{D.}$ 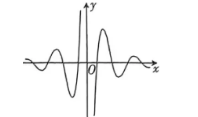
定义函数 $\min \{f(x), g(x)\}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}f(x), f(x) \leqslant g(x), \\ g(x), f(x)>g(x),\end{array}, \quad\right.$ (x) $\min \left\{|x|-1, x^2-2 a x+a+2\right\}$, 若 $h(x)=0$ 至少有 3 个不同的解, 则实数 $a$ 的取值范围是
$\text{A.}$ $[1,2]$
$\text{B.}$ $[2,3]$
$\text{C.}$ $[3,4]$
$\text{D.}$ $[4,5]$
溶液酸碱度是通过 $P H$ 计量的, $P H$ 的计算公式为 $P H=-\lg \left[H^{+}\right]$, 其中 $\left[H^{+}\right]$表示溶液中氢离子的浓度, 单位是摩尔/升. 已知某 溶液的 $P H$ 值为 2.921 , 则该溶液中氢离子的浓度约为 ( 取 $\lg 2=0.301, \lg 3=0.477)$
$\text{A.}$ $1.2 \times 10^{-3}$ 摩尔/升
$\text{B.}$ $1.2 \times 10^{-4}$ 摩尔/升
$\text{C.}$ $6 \times 10^{-3}$ 摩尔/升
$\text{D.}$ $6 \times 10^{-4}$ 摩尔/升
若函数 $f(x)=4 \cos (2 x+\varphi)-2 \sqrt{2}(0 \leq \varphi \leq \pi)$ 在 $\left[0, \frac{11 \pi}{6}\right]$ 内恰有 4 个零点, 则 $\varphi$ 的取值范围是
$\text{A.}$ $\left[0, \frac{\pi}{4}\right] \cup\left[\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{7 \pi}{12}\right]$
$\text{B.}$ $\left[\frac{\pi}{12}, \frac{\pi}{4}\right] \cup\left[\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{7 \pi}{12}\right]$
$\text{C.}$ $\left[0, \frac{\pi}{4}\right] \cup\left[\frac{7 \pi}{12}, \pi\right]$
$\text{D.}$ $\left[\frac{\pi}{12}, \frac{\pi}{4}\right] \cup\left[\frac{7 \pi}{12}, \pi\right]$
恩格尔系数 $n=\frac{\text { 食品消费支出总额 }}{\text { 消费支出,总额 }} \times 100 \%$, 国际上常用恩格尔系数 $n$ 来衡量一个地
区家庭的富裕程度, 恩格尔系数越低, 人民生活越富裕. 某地区家庭 2022 年底恩格尔系 数 $n$ 为 $50 \%$, 刚达到小康, 预计从 2023 年起该地区家庭每年消费支出总额增加 $30 \%$, 食 品消费支出总额缯加 $20 \%$, 依据以上数据, 预计该地区家庭恩格尔系数 $n$ 满足 $30 \% < n \leq 40 \%$ 达到富裕水平, 至少经过 ( ) 年 (参考数据: $\lg 0.6 \approx-0.22, \lg 0.8 \approx-0.10, \lg 12 \approx 1.08$, $\lg 13 \approx 1.11)$
$\text{A.}$ 8年
$\text{B.}$ 7年
$\text{C.}$ 4年
$\text{D.}$ 3年