单选题 (共 6 题 ),每题只有一个选项正确
电影《流浪地球》中反复出现这样的人工语音: “道路干万条, 安全第一条, 行车不规范, 辛人两 行泪” 成为网络热句.讲的是 “开车不喝酒, 喝酒不开车” 2019 年, 公安部交通管理局下发《关于治理酒驾醉驾违法犯罪行为的指导意见》, 对综合治理酒驾醉驾违法犯罪行为提出了新规定, 根据国家质量监督检验检疫总局下发的标准, 车辆驾驶人员饮酒后或者醉酒后驾车血液中的酒精含量阈值见表.经过反复试验, 一般情况下, 某人喝一瓶筥酒后酒精在人体血液中的变化规律的“散点图”见图,
且图表所示的函数模型 $y=\left\{\begin{array}{l}40 \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{3} x\right)+13,0 \leq x < 2 \\ 90 \cdot e^{-0.5 x}+14, x \geq 2\end{array}\right.$, 假设该人喝一瓶㗭酒后至少经过
$n\left(n \in N^{*}\right)$ 小时才可以驾车,则 $n$ 的值为(参考数据: $\ln 15 \approx 2.71, \ln 30 \approx 3.40$ ) ( )

$\text{A.}$ $5$
$\text{B.}$ $6$
$\text{C.}$ $7$
$\text{D.}$ $8$
汽车经过启动、加速行驶、匀速行驶、减速行驶之后停车, 若把这 一过程中汽车的行驶路程 $\mathrm{s}$ 看作时间 $\mathrm{t}$ 的函数, 其图象可能是 ( )
$\text{A.}$ 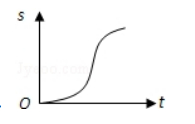 $\text{B.}$
$\text{B.}$ 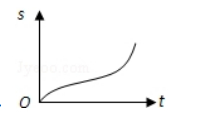 $\text{C.}$
$\text{C.}$ 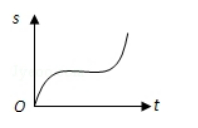 $\text{D.}$
$\text{D.}$ 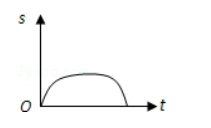
若函数 $y=f(x)$ 的图象与函数 $y=\ln \sqrt{x}+1$ 的图象关于直线 $y=x$ 对称, 则 $f(x)=$ ( )
$\text{A.}$ $\mathrm{e}^{2 \mathrm{x}-2}$
$\text{B.}$ $\mathrm{e}^{2 \mathrm{x}}$
$\text{C.}$ $\mathrm{e}^{2 \mathrm{x}+1}$
$\text{D.}$ $\mathrm{e}^{2 \mathrm{x}+2}$
已知曲线 $y=\frac{x+1}{x-1}$ 在点 $(3,2$ ) 处的切线与直线 $a x+y+1=0$ 垂直, 则 $a$ 的值为 $($ )
$\text{A.}$ $2$
$\text{B.}$ $\frac{1}{2}$
$\text{C.}$ $-\frac{1}{2}$
$\text{D.}$ $-2$
设偶函数 $f(x)$ 满足 $f(x)=2^{x}-4(x \geqslant 0)$ ,则 $\{x \mid f(x-2)>0\}=$ ( )
$\text{A.}$ $\{x \mid x < -2$ 或 $x>4\}$
$\text{B.}$ $\{x \mid x < 0$ 或 $x>4\}$
$\text{C.}$ $\{x \mid x < 0$ 或 $x>6\}$
$\text{D.}$ $\{x \mid x < -2$ 或 $x>2\}$
下列函数中, 既是偶函数又在 $(0,+\infty)$ 上单调递增的函数是( )
$\text{A.}$ $y=2 x^{3}$
$\text{B.}$ $y=|x|+1$
$\text{C.}$ $y=-x^{2}+4$
$\text{D.}$ $y=2^{-|x|}$